Stay Afloat: Master Safety and Self-Rescue on the Water






Read the Water Before You Launch
Gear That Guards You
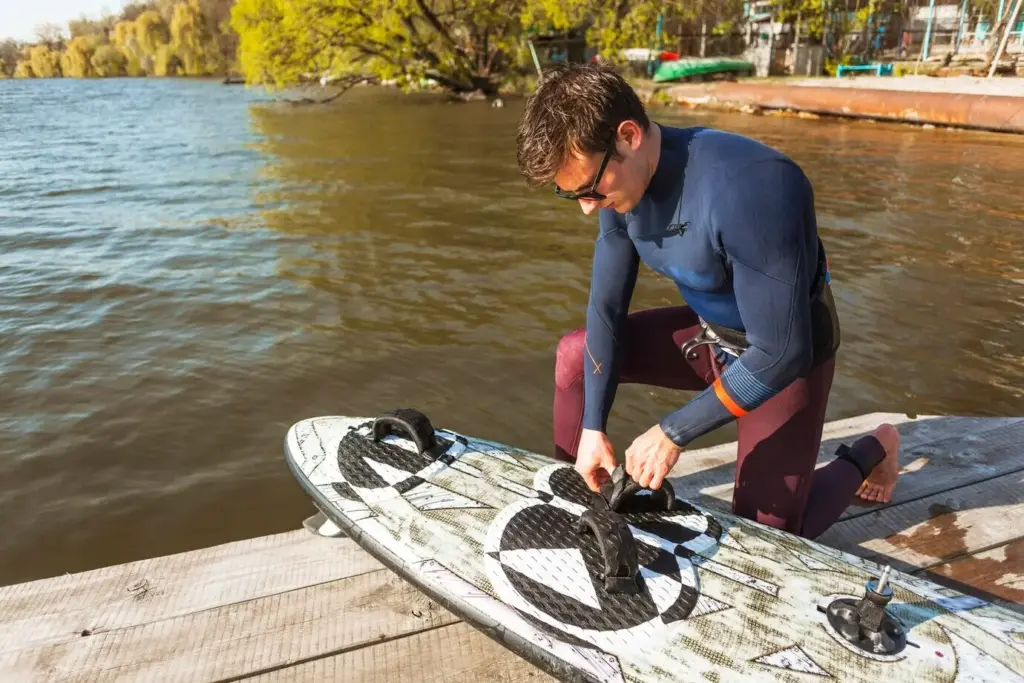


PFD Fit That You’ll Actually Wear
Choose a PFD with unrestricted shoulder movement, low-profile foam, and secure, non-slip straps. Try it in the water to confirm flotation position and comfort when wet. Keep rescue knives tethered and accessible. Stash whistle, signaling mirror, and snacks in pockets. A comfortable, familiar PFD means it stays on all day, without negotiation.


Dress for the Water, Not the Air
Cold shock happens fast, even under sunny skies, so layer with purpose. Neoprene or a drysuit with proper base layers preserves muscle function and decision-making. Bring a warm hat, wind shell, and spare insulation in a dry bag. Wet hands lose dexterity quickly, so pack gloves. Comfort breeds better paddling decisions and steadier rescues.



Get Back In: Self-Rescue Fundamentals
If You Swim: Control the Chaos

Avoid Foot Entrapment and Strainers
In moving water, keep feet up near the surface and point them downstream to shield your body. Never stand in fast current until you can feel stable, shallow footing. Give strainers a wide berth, ferrying laterally early, not late. Training yourself to default to safe swimming posture turns instinctive panic into structured survival.

Defensive vs. Aggressive Swimming
Defensive swimming preserves energy while protecting your body, whereas aggressive bursts help you cross eddy lines or escape hazards. Switch modes intentionally, not reactively. Use strong ferry angles, quick sculling strokes, and short rests in sheltered water. Practicing transitions in controlled settings teaches you to move decisively when seconds truly matter.

Breathing Through Cold Shock
Cold water triggers an involuntary gasp and rapid breathing. Fight the impulse by counting slow, deliberate exhales while floating stable. Give yourself sixty seconds before attempting complex tasks. Rehearse this response in supervised conditions so your brain recognizes the sensation. Calm breath becomes your life raft when clarity briefly vanishes in icy water.
Teamwork Makes the Rescue Work
Field First Aid You’ll Really Use
Recognize and Reverse Hypothermia
Practice That Sticks
Short, Focused Drills Build Real Skill
Warm up with balance and edging, then spend fifteen concentrated minutes on a single rescue step. Repeat under small variations: different winds, gloves, or loaded boats. End with a confidence drill you always nail. This rhythm builds trust in your abilities and keeps improvement measurable, motivating, and anchored in real-world conditions.
Simulations and Story-Driven Scenarios
Create realistic mini-adventures: a surprise capsize near a pier, a lost paddle, or thick fog at dusk. Assign roles and rotate responsibilities. Debrief immediately, highlighting timing, communication, and energy management. These story-shaped practices make lessons memorable and prepare minds and muscles to respond coherently when genuine uncertainty arrives unannounced.